Attorneys: Alan Eugene Miller endured ‘torture’ during execution attempt
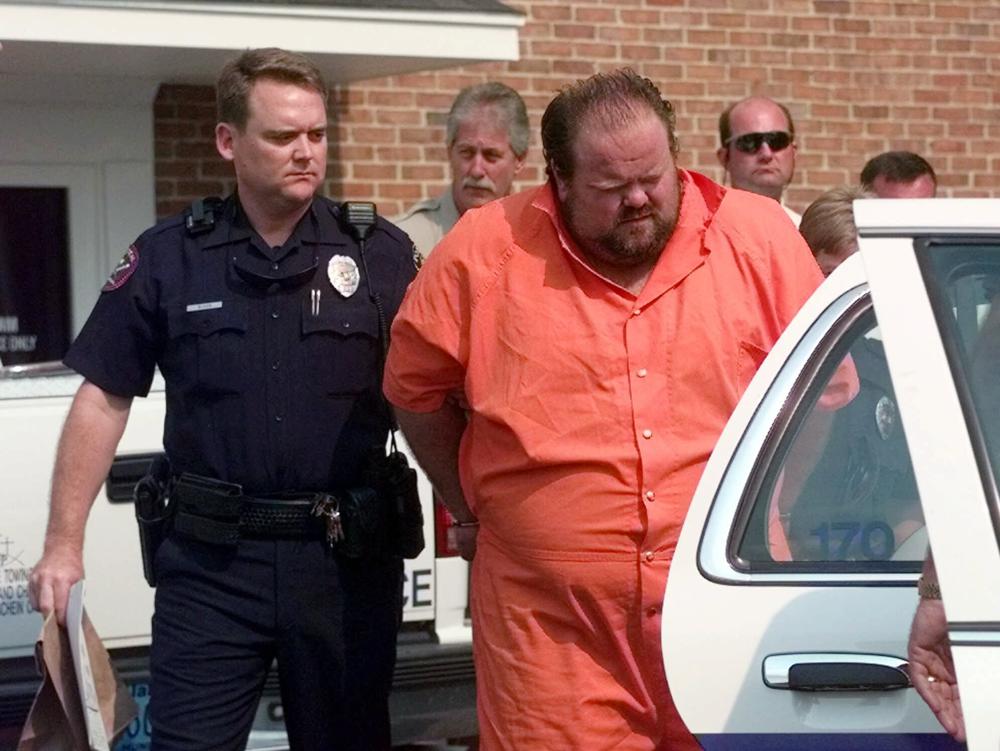

An Alabama inmate said prison staff poked him with needles for over an hour as they tried to find a vein during an aborted lethal injection last month. At one point, they left him hanging vertically on a gurney before state officials made the decision to call off the execution. Attorneys for 57-year-old Alan Eugene Miller wrote about his experience during Alabama’s September 22 execution attempt in a court filing made last week. Miller’s attorneys are trying to block the state from attempting a second lethal injection. Two men in scrubs used needles to repeatedly probe Miller’s arms, legs, feet, and hands. At one point, using a cell phone flashlight to help their search for a vein, according to the October 6 court filing. The attorneys called Miller the “only living execution survivor in the United States” and said Alabama subjected Miller “to precisely the unnecessary and wanton infliction of pain that the Eighth Amendment was intended to prohibit.” Alabama has asked the state Supreme Court to set a new execution date for Miller, saying the execution was canceled only because of a time issue as the state faced a midnight deadline to get the lethal injection underway. “Despite this failed execution, the physical and mental torture it inflicted upon Mr. Miller, and the fact that Defendants have now botched three lethal injection executions in just four years, Defendants relentlessly seek to execute Mr. Miller again—presumably by lethal injection,” attorneys for Miller wrote, referencing an execution that was canceled and another that took three hours to get underway. “What then, in Defendants’ view, is a constitutional amount of time to spend stabbing someone with needles in an attempt to kill them?” his attorneys wrote. The 351-pound (159-kilogram) inmate testified in an earlier court hearing that medical workers always have difficulty accessing his veins, and that is why he wanted to be executed by nitrogen hypoxia, a newly approved execution method that the state has yet to try. Miller said he was led into the execution chamber at 10 p.m., about an hour after the U.S. Supreme Court lifted an injunction that had been blocking the lethal injunction, and was strapped to the gurney at about 10:15 p.m. After the two men used needles to probe various parts of his body for a vein, also using a phone flashlight to help, Miller told the men, “he could feel that they were not accessing his veins, but rather stabbing around his veins.” Later, a third man then began slapping his neck in an apparent attempt to look for a vein. The three men in scrubs stopped their probing and left the chamber after there was a loud knock on a death chamber window from the state’s observation room, according to the court filing. A prison officer then raised the gurney to a vertical position. Miller said the wall clock read 11:40 p.m., and he estimated that he hung there for about 20 minutes before he was let down and told that his execution was canceled for the evening. “Mr. Miller felt nauseous, disoriented, confused, and fearful about whether he was about to be killed, and was deeply disturbed by his view of state employees silently staring at him from the observation room while he was hanging vertically from the gurney. Blood was leaking from some of Mr. Miller’s wounds,” the motion stated. Miller was sentenced to death after being convicted of a 1999 workplace rampage in which he killed Terry Jarvis, Lee Holdbrooks, and Scott Yancy. “Due to the lateness of the hour, the Alabama Department of Corrections was limited in the number of attempts to gain intravenous access it could make. ADOC made the decision to halt its efforts to obtain IV access at approximately 11:30 p.m., resulting in the expiration of the court’s execution warrant,” the state attorney general’s office wrote in the request for a new date. This is at least the third time Alabama has acknowledged problems with vein access during a lethal injection. The state’s July execution of Joe Nathan James took more than three hours to get underway. Alabama called off the 2018 execution of Doyle Hamm after being unable to establish an intravenous line. Republished with the permission of The Associated Press.
Alabama seeks new execution date for Alan Miller

Alabama is asking a court to swiftly set a new execution date for an inmate who had his lethal injection called off last month after multiple failed attempts to connect an intravenous line to the man’s veins. The Alabama attorney general’s office, in the Tuesday court filing, asked the Alabama Supreme Court to set a new execution date for Alan Eugene Miller. The state did not give a timeframe but asked the justices to take the matter up before deciding a pending execution date request involving another inmate. The Alabama Department of Corrections attempted to put Miller to death on September 22, but officials called off the lethal injection after the execution team was unable to connect the intravenous line. The state faced a midnight deadline to get the execution underway before the death warrant expired. Miller, 57, was sentenced to death after being convicted of a 1999 workplace rampage in which he killed Terry Jarvis, Lee Holdbrooks, and Scott Yancy. Miller’s attorneys are expected to fight the effort to set a new execution date. U.S. District Judge R. Austin Huffaker Jr., at the request of Miller’s attorneys, ordered Alabama to preserve notes and medical materials from the failed execution attempt. Court documents have not disclosed exactly how long the state tried to connect an IV line to Miller. However, a lawyer for the prison system told Huffaker that there had been multiple attempts in the approximately 2.5 hours that elapsed between the U.S. Supreme Court clearing the way for the execution shortly after 9 p.m. and the state calling it off at about 11:30 p.m. “Due to the lateness of the hour, the Alabama Department of Corrections was limited in the number of attempts to gain intravenous access it could make. ADOC made the decision to halt its efforts to obtain IV access at approximately 11:30 p.m., resulting in the expiration of the court’s execution warrant,” the state attorney general’s office wrote in the request for a new date. This is at least the third time Alabama has acknowledged problems with venous access during a lethal injection. The state’s July execution of Joe Nathan James took more than three hours to get underway. Alabama called off the 2018 execution of Doyle Hamm after being unable to establish an intravenous line. Republished with the permission of The Associated Press.
Alabama sets execution date for Kenneth Eugene Smith
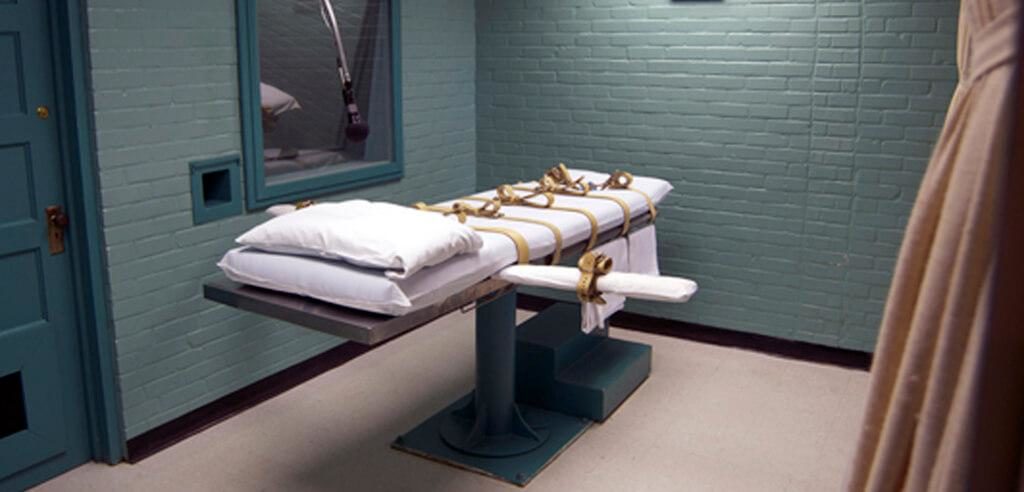
Alabama has set a November execution date for a man convicted in the 1988 murder-for-hire killing of a pastor’s wife. The scheduled execution follows criticism over the state’s last two lethal injection attempts, including one that was called off after the execution team had trouble finding a vein. Kenneth Eugene Smith, 57, is set to die at Holman Correctional Facility on November 17, according to a Friday order from the Alabama Supreme Court. Smith was sentenced to death for the killing of Elizabeth Dorlene Sennett, a 45-year-old grandmother and pastor’s wife. Prosecutors said Smith was one of two men who were each paid $1,000 to kill Sennett on behalf of her husband, the Rev. Charles Sennett, who was deeply in debt and wanted to collect on insurance. Elizabeth Sennett was found dead on March 18, 1988, in the couple’s home in Colbert County. The coroner testified that she had been stabbed eight times in the chest and once on each side of the neck. The pastor killed himself a week later. Smith maintained it was the other man who stabbed Elizabeth Sennett, according to court documents. Smith was initially convicted in 1989, and a jury voted 10-2 to recommend a death sentence, which a judge imposed. His conviction was overturned on appeal in 1992. He was retried and convicted again in 1996. This time, the jury recommended a life sentence by a vote of 11-1, but a judge overrode the jury’s recommendation and sentenced Smith to death. Alabama no longer allows a judge to override a jury’s recommendation. In 2017, Alabama became the last state to abolish the practice of letting judges override a jury’s sentencing recommendation in death penalty cases, but the change was not retroactive and therefore did not affect death row prisoners like Smith. John Forrest Parker, the other man that prosecutors said was paid to kill Elizabeth Sennett, was executed in 2010. When asked if he had any final words, Parker turned his head to face Mike and Charles Sennett, the victim’s sons, and said, “I’m sorry. I don’t ever expect you to forgive me. I really am sorry.” Alabama last month called off the execution of Alan Miller because of difficulty accessing the inmate’s veins. Alabama Corrections Commissioner John Hamm told reporters that “accessing the veins was taking a little bit longer than we anticipated,” and the state did not have sufficient time to get the execution underway by a midnight deadline. That was at least the third time Alabama has acknowledged problems with venous access during a lethal injection. The state’s July execution of Joe Nathan James took more than three hours to get underway. And, in 2018, Alabama called off the execution of Doyle Hamm after being unable to establish an intravenous line. Republished with the permission of The Associated Press.

