7 Republicans vote to convict Donald Trump in impeachment trial

Seven Republicans voted Saturday to convict former President Donald Trump in his Senate trial, easily the largest number of lawmakers to ever vote to find a president of their own party guilty at impeachment proceedings. While lawmakers acquitted Trump of inciting the Jan. 6 Capitol attack, they voted 57-43 to convict him — short of the two-thirds majority needed to find him guilty. Still, with seven Republicans joining all 50 Democrats in voting “guilty,” the Senate issued an unmistakable bipartisan chorus of condemnation of the former president that could have political implications for a GOP conflicted over its future. “If I can’t say what I believe that our president should stand for, then why should I ask Alaskans to stand with me?” Sen. Lisa Murkowski of Alaska told reporters. Besides Murkowski, other Republican senators voting against Trump were Richard Burr of North Carolina, Bill Cassidy of Louisiana, Susan Collins of Maine, Mitt Romney of Utah, Ben Sasse of Nebraska, and Patrick Toomey of Pennsylvania. Underscoring the perils of affronting Trump and his legions of GOP loyalists, by late evening top Republicans from at least two of the defecting senators’ states had blasted them. Pennsylvania GOP Chairman Lawrence Tabas issued a statement saying he shared “the disappointment of many of our grassroots leaders and volunteers” over Toomey’s vote. Louisiana’s Republican Party said, “We condemn, in the strongest possible terms” Cassidy’s vote and said its executive committee voted unanimously to censure him. Democrats holding out long-shot hopes of convicting Trump would have needed 17 Republicans to prevail, which as expected proved an unreachable goal. That hope died after the influential Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell, R-Ky., said he would vote to acquit because he believed lawmakers had no jurisdiction over a former president. Even so, McConnell delivered searing words against Trump in a speech after the vote, saying the former president was “practically and morally responsible” for provoking the attack on lawmakers as they formally certified Trump’s Electoral College defeat by Joe Biden. Five people died, and the House impeached Trump for inciting insurrection. Most of the defecting Republicans had clashed with Trump over the years. Burr and Toomey have said they will retire and not seek reelection when their terms expire next year, and Murkowski and Collins have histories of clashing with Trump over health care and other policies. Perhaps the day’s most surprising GOP defector was Burr, a 16-year Senate veteran who keeps a low profile in Washington and after years as top Republican on the Senate Intelligence Committee is used to telegraphing little about his views. Burr, 65, will not seek reelection next year and will retire. In a written statement, he said Trump made unfounded claims about a fraud-riddled election “because he did not like the results.” He said Trump used the presidency to “inflame” the rioters rather than urging them to stand down. “The evidence is compelling that President Trump is guilty of inciting an insurrection against a coequal branch of government,” Burr said. Also striking was the “guilty” vote by Cassidy, who was reelected in November from a deep-red state where GOP support is widespread. Cassidy, 63 and a physician, had initially sided with the vast majority of Senate Republicans who voted last month to block the trial from moving forward. But he blasted a shambolic performance by Trump’s legal team at the start of the trial while praising Democrats for presenting a compelling case. “Our Constitution and our country is more important than any one person. I voted to convict President Trump because he is guilty,” Cassidy said in a one-sentence statement issued after his vote to convict. Toomey, a traditional conservative, decried Trump’s efforts to overturn election results — Trump’s targets include Toomey’s Pennsylvania — and to encourage his supporters’ march on the Capitol. “All of this to hold on to power despite having legitimately lost,” Toomey said. He said that because of Trump’s actions, “for the first time in American history, the transfer of presidential power was not peaceful” and said Trump had “betrayed the confidence millions of us placed in him.” Sasse has long criticized Trump’s authoritarian streak. Last week he excoriated pro-Trump Republican Party officials in his home state, telling them in a video message that “politics isn’t about the weird worship of one dude.” “Tribalism is a hell of a drug, but our oath to the Constitution means we’re constrained to the facts,” Sasse said Saturday. He said he wouldn’t vote against his own conscience “simply because it is politically convenient.” Romney’s “guilty” vote at Trump’s initial impeachment trial last February made him the first senator to ever vote to convict a president of the same party. The trial that ended Saturday was Trump’s second — making him the first president to ever be tried twice for impeachment — and the fourth in presidential history. Presidents Andrew Johnson in 1868 and Bill Clinton in 1999 were acquitted and received unanimous support from their Democratic Party. Republished with the permission of the Associated Press.
Donald Trump trial video shows vast scope, danger of Capitol riot

Prosecutors unveiled chilling new security video in Donald Trump’s impeachment trial on Wednesday, showing the mob of rioters breaking into the Capitol, smashing windows and doors, and searching menacingly for Vice President Mike Pence and House Speaker Nancy Pelosi as overwhelmed police begged on their radios for help. In the previously unreleased recordings, the House prosecutors displayed gripping scenes of how close the rioters were to the country’s leaders, roaming the halls chanting “Hang Mike Pence,” some equipped with combat gear. Outside, the mob had set up a makeshift gallows. Videos of the siege have been circulating since the day of the riot, but the graphic compilation amounted to a more complete narrative, a moment-by-moment retelling of one of the nation’s most alarming days. In addition to the evident chaos and danger, it offered fresh details on the attackers, scenes of police heroism, and cries of distress. And it showed just how close the country came to a potential breakdown in its seat of democracy as Congress was certifying Trump’s election defeat to Democrat Joe Biden. “They did it because Donald Trump sent them on this mission,” said House prosecutor Stacey Plaskett, the Democratic delegate representing the U.S. Virgin Islands. “His mob broke into the Capitol to hunt them down.” The stunning presentation opened the first full day of arguments in the trial as the prosecutors argued Trump was no “innocent bystander” but rather the “inciter in chief” of the deadly Capitol riot, a president who spent months spreading election lies and building a mob of supporters primed for his call to stop Biden’s victory. Though most of the Senate jurors have already made up their minds on acquittal or conviction, they were riveted and sat silently. Screams from the audio and video filled the Senate chamber. Senators shook their heads, folded their arms, and furrowed their brows. One Republican, James Lankford of Oklahoma, bent his head, a GOP colleague putting his hand on his arm in comfort. “On Jan. 6, President Trump left everyone in this Capitol for dead,” said Rep. Joaquin Castro, D-Texas, a prosecutor. Pence, who had been presiding over a session to certify Biden’s victory over Trump — thus earning Trump’s criticism — is shown being rushed to safety, sheltered in an office with his family just 100 feet from the rioters. Pelosi was evacuated from the complex before the mob prowls her suite of offices, her staff hiding quietly behind closed doors. At one dramatic moment, the video shows police shooting into the crowd through a broken window, killing a San Diego woman, Ashli Babbitt. In another, a police officer is seen being crushed by the mob. Police overwhelmed by the rioters frantically announce “we lost the line” and urge officers to safety. One officer later died. Some senators acknowledged it was the first time they had grasped how perilously close the country came to serious danger. “When you see all the pieces come together, just the total awareness of that, the enormity of this threat, not just to us as people, as lawmakers, but the threat to the institution and what Congress represents, it’s disturbing,” said Republican Sen. Lisa Murkowski of Alaska. “Greatly disturbing.” Trump is the first president to face an impeachment trial after leaving office and the first to be twice impeached. He is charged with incitement of insurrection through fiery words his defense lawyers say are protected by the Constitution’s First Amendment and just figures of speech. The House Democrats showed piles of evidence from the former president himself — hundreds of Trump tweets and comments that culminated in his Jan. 6 rally cry to go to the Capitol and “fight like hell” to overturn his defeat. Trump then did nothing to stem the violence and watched with “glee,” they said, as the mob ransacked the iconic building. “To us, it may have felt like chaos and madness, but there was method to the madness that day,” said Rep. Jamie Raskin, D-Md., the lead prosecutor, who pointed to Trump as the instigator. “And when his mob overran and occupied the Senate and attacked the House and assaulted law enforcement, he watched it on TV like a reality show. He reveled in it.” In one scene, a Capitol Police officer redirects Sen. Mitt Romney, R-Utah, down a hallway to avoid the mob. It was the same officer, Eugene Goodman, who has been praised as a hero for having lured rioters away from the Senate doors. “It tears at your heart and brings tears to your eyes,” Romney said after watching the video. He said he didn’t realize how close he had been to danger. The day’s proceedings unfolded after Tuesday’s emotional start that left the former president fuming when his attorneys delivered a meandering defense and failed to halt the trial on constitutional grounds. Some allies called for yet another shakeup to his legal team. The prosecutors are arguing that Trump’s words were part of “the big lie” — his relentless efforts to sow doubts about the election results, revving up his followers to “stop the steal” even though there was no evidence of substantial fraud. Trump knew very well what would happen when he took to the microphone at the outdoor White House rally that day as Congress gathered to certify Biden’s win, said Rep. Joe Neguse, D-Colo, another impeachment manager. “This was not just a speech,” he said. Security remained extremely tight Wednesday at the Capitol, fenced off and patrolled by National Guard troops. White House press secretary Jen Psaki has said Biden would not be watching the trial. The difficulty facing Trump’s defenders became apparent at the start as they leaned on the process of the trial rather than the substance of the case against him. They said the Constitution doesn’t allow impeachment at this late date after he has left the White House. Even though the Senate rejected that argument in Tuesday’s vote to proceed, the legal issue could resonate with Republicans eager to acquit Trump without being seen as condoning his behavior. Defense
Senate Republicans back Donald Trump as impeachment trial nears

Donald Trump’s defenders in the Senate on Sunday rallied around the former president before his impeachment trial, dismissing it as a waste of time and arguing that the former president’s fiery speech before the U.S. Capitol insurrection does not make him responsible for the violence of Jan. 6. “If being held accountable means being impeached by the House and being convicted by the Senate, the answer to that is no,” said Republican Sen. Roger Wicker of Mississippi, making clear his belief that Trump should and will be acquitted. Asked if Congress could consider other punishment, such as censure, Wicker said the Democratic-led House had that option earlier but rejected it in favor of impeaching him. “That ship has sailed,” he said. The Senate is set to launch the impeachment trial Tuesday to consider the charge that Trump’s fighting words to protesters at a Capitol rally, as well as weeks of falsehoods about a stolen and rigged presidential election, provoked a mob to storm the Capitol. Five people died as a result of the melee, including a police officer. Many senators including Senate Republican leader Mitch McConnell immediately denounced the violence and pointed a finger of blame at Trump. Following the riot, Wicker said Americans “will not stand for this kind of attack on the rule of law” and without naming names, said “we must prosecute” those who undermine democracy. But with Trump now gone from the presidency, Republicans have shown little political appetite to take further action, such as an impeachment conviction that could lead to barring him from running for future office. Those partisan divisions appear to be hardening ahead of Trump’s trial, a sign of his continuing grip on the GOP. On Sunday, Wicker described Trump’s impeachment trial as a “meaningless messaging partisan exercise.” When asked if Trump’s conduct should be more deserving of impeachment than President Bill Clinton’s, whom Wicker voted to impeach, he said: “I’m not conceding that the President Trump incited an insurrection.” Clinton’s impeachment, in 1998, was sparked by his false denial in a deposition of a sexual relationship with a White House intern. Republican Sen. Rand Paul of Kentucky dismissed Trump’s trial as a farce with “zero chance of conviction,” describing Trump’s words to protesters to “fight like hell” as Congress was voting to ratify Joe Biden’s presidential victory as “figurative” speech. “If we’re going to criminalize speech, and somehow impeach everybody who says, ‘Go fight to hear your voices heard,’ I mean really we ought to impeach Chuck Schumer then,” Paul said, referring to the now Democratic Senate majority leader and his criticisms of Justices Neil Gorsuch and Brett Kavanaugh. “He went to the Supreme Court, stood in front of the Supreme Court, and said specifically, ‘Hey Gorsuch, Hey Kavanaugh, you’ve unleashed a whirlwind. And you’re going to pay the price.’” Paul noted that Chief Justice John Roberts had declined to preside over this week’s impeachment proceeding because Trump was no longer president. Democratic Sen. Patrick Leahy of Vermont will preside over the trial as Senate president pro tempore. “It is a farce, it is unconstitutional. But more than anything it’s unwise, and going to divide the country,” Paul said. Last month, Paul forced a vote to set aside the trial as unconstitutional because Trump is no longer in office, which legal experts say is disputable. But the vote suggested the near impossibility in reaching a conviction in a Senate where Democrats hold 50 seats but a two-thirds vote — or 67 senators — would be needed to convict Trump. Forty-four Republican senators sided with Paul and voted to oppose holding an impeachment trial at all. Five Republican senators joined with Democrats to reject Paul’s motion: Mitt Romney of Utah, Ben Sasse of Nebraska, Susan Collins of Maine, Lisa Murkowski of Alaska, and Pat Toomey of Pennsylvania. Some Republicans have said the vote doesn’t “bind” them into voting a particular way on conviction, with Republican Sen. Bill Cassidy of Louisiana saying Sunday he would listen carefully to the evidence. But even Trump’s sharper GOP critics on Sunday acknowledged the widely expected outcome. “You did have 45 Republican senators vote to suggest that they didn’t think it was appropriate to conduct a trial, so you can infer how likely it is that those folks will vote to convict,” said Toomey, who has made clear he believes Trump committed “impeachable offenses.” “I still think the best outcome would have been for the president to resign” before he left office, he said. “Obviously he chose not to do that.” Republican Sen. Lindsey Graham of South Carolina, one of Trump’s ardent defenders, said he believes Trump’s actions were wrong and “he’s going to have a place in history for all of this,” but insisted it’s not the Senate’s job to judge. “It’s not a question of how the trial ends, it’s a question of when it ends,” Graham said. “Republicans are going to view this as an unconstitutional exercise, and the only question is, will they call witnesses, how long does the trial take? But the outcome is really not in doubt.” Wicker spoke on ABC’s “This Week,” Paul was on “Fox News Sunday,” Toomey appeared on CNN’s “State of the Union,” and Graham was on CBS’ “Face the Nation.” Republished with the permission of the Associated Press.
Joe Biden meets Republicans on virus aid, but no quick deal
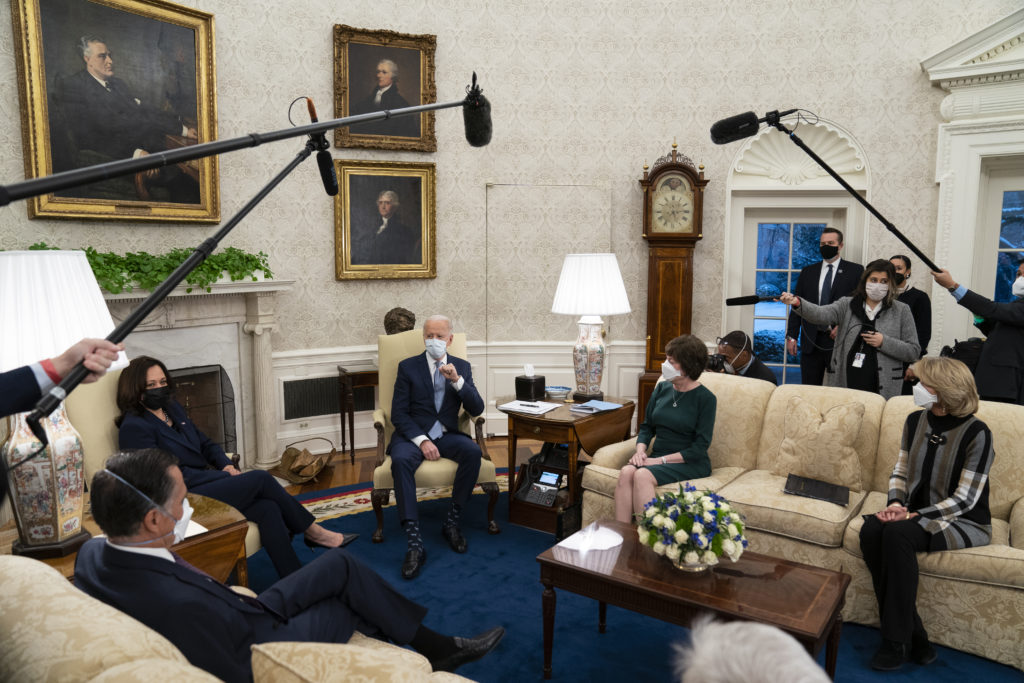
President Joe Biden told Republican senators during a two-hour meeting Monday night he’s unwilling to settle on an insufficient coronavirus aid package after they pitched their slimmed-down $618 billion proposal that’s a fraction of the $1.9 trillion he is seeking. No compromise was reached in the lengthy session, Biden’s first with lawmakers at the White House, and Democrats in Congress pushed ahead with groundwork for approving his COVID relief plan with or without Republican votes. Despite the Republican group’s push for bipartisanship, appealing to Biden’s efforts to unify the country, the president made it clear he won’t delay aid in hopes of winning GOP support. White House Press Secretary Jen Psaki said that while there were areas of agreement, “the president also reiterated his view that Congress must respond boldly and urgently, and noted many areas which the Republican senators’ proposal does not address.” She said, “He will not slow down work on this urgent crisis response, and will not settle for a package that fails to meet the moment.” The two sides are far apart, with the Republican group of 10 senators focused primarily on the health care crisis and smaller $1,000 direct aid to Americans, and Biden leading Democrats toward a more sweeping rescue package, three times the size, to shore up households, local governments, and a partly shuttered economy. On a fast track, the goal is to have COVID relief approved by March, when extra unemployment assistance and other pandemic aid expires, testing the ability of the new administration and Congress to deliver, with political risks for all sides from failure. Republican Sen. Susan Collins of Maine called the meeting a “frank and very useful” conversation, noting that the president also filled in some details on his proposal. “All of us are concerned about struggling families, teetering small businesses, and an overwhelmed health care system,” said Collins, flanked by other senators outside the White House. Republicans are tapping into bipartisan urgency to improve the nation’s vaccine distribution and vastly expand virus testing with $160 billion in aid. That is similar to what Biden has proposed. But from there, the two plans drastically diverge. The GOP’s $1,000 direct payments would go to fewer households than the $1,400 Biden has proposed, and the Republicans offer only a fraction of what he wants to reopen schools. They also would give nothing to states, money that Democrats argue is just as important, with $350 billion in Biden’s plan to keep police, fire, and other workers on the job. Gone are Democratic priorities such as a gradual lifting of the federal minimum wage to $15 an hour. Wary Democrats pushed ahead at the Capitol, unwilling to take too much time in courting GOP support that may not materialize or in delivering too meager a package that they believe doesn’t address the scope of the nation’s health crisis and economic problems. Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer warned that history is filled with “the costs of small thinking.” House and Senate Democrats released a separate budget resolution Monday a step toward approving Biden’s package with a “budget reconciliation” process that wouldn’t depend on Republican support for passage. “The cost of inaction is high and growing, and the time for decisive action is now,” Schumer and Speaker Nancy Pelosi said in a statement. The accelerating talks came as the Congressional Budget Office delivered mixed economic forecasts Monday with robust growth expected at a 4.5% annual rate but employment rates not to return to pre-pandemic levels for several years. The overture from the coalition of 10 GOP senators, mostly centrists, was an attempt to show that at least some in the Republican ranks want to work with Biden’s new administration, rather than simply operating as the opposition in the minority in Congress. But in echoes of the 2009 financial crisis, Democrats warn against too small a package as they believe happened during the Obama administration’s attempt to pull the nation toward recovery. Psaki said earlier Monday there is “obviously a big gap” between the $1.9 trillion package Biden has proposed and the $618 billion counteroffer. An invitation to the GOP senators to meet with Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris at the White House came hours after the lawmakers sent Biden a letter on Sunday urging him to negotiate rather than try to ram through his relief package solely on Democratic votes. “We share many of your priorities,” the senators wrote releasing their plan. The cornerstone of the GOP plan is $160 billion for the health care response — vaccine distribution, a “massive expansion” of testing, protective gear, and funds for rural hospitals, according to a draft. It includes $20 billion to reopen schools compared to $170 billion in Biden’s plan. The Republicans offer $40 billion for Paycheck Protection Program business aid. Under the GOP proposal, $1,000 direct payments would go to individuals earning up to $40,000 a year, or $80,000 for couples. The proposal would begin to phase out the benefit after that, with no payments for individuals earning more than $50,000, or $100,000 for couples. That’s less than Biden’s proposal of $1,400 direct payments at higher income levels, up to $300,000 for some households. The meeting, though private, was Biden’s most public involvement in the negotiations. Winning the support of 10 Republicans would be significant for Biden, potentially giving him the votes needed in the 50-50 Senate where Harris is the tie-breaker. The more liberal wing of his party wants to push the relief package through the budget reconciliation process, which would allow the bill to pass with a 51-vote majority in the Senate, rather than the 60 votes typically needed to advance. The White House remains committed to exploring avenues for bipartisanship even as it prepares for Democrats to move alone on a COVID relief bill, according to a senior administration official granted anonymity to discuss the private thinking. At the same time, the White House may be willing to adjust its ask, perhaps shifting some less virus-oriented aspects into a package that is set to go next before Congress, the
GOP lawmakers urge Joe Biden to meet with them on virus relief

Ten Republican senators on Sunday proposed spending about one-third of what President Joe Biden is seeking in coronavirus aid and urged him to negotiate rather than try to ram through his $1.9 trillion package solely on Democratic votes. In challenging Biden to fulfill his pledge of unity, the group said in a letter that their counterproposal will include $160 billion for vaccines, testing, treatment, and personal protective equipment and will call for more targeted relief than Biden’s plan to issue $1,400 stimulus checks for most Americans. Winning the support of 10 Republicans would be significant for Biden in the 50-50 Senate where Vice President Kamala Harris is the tie-breaker. If all Democrats were to back an eventual compromise bill, the legislation would reach the 60-vote threshold necessary to overcome potential blocking efforts and pass under regular Senate procedures. “In the spirit of bipartisanship and unity, we have developed a COVID-19 relief framework that builds on prior COVID assistance laws, all of which passed with bipartisan support,” the Republican senators wrote. “Our proposal reflects many of your stated priorities, and with your support, we believe that this plan could be approved quickly by Congress with bipartisan support.” The plea for Biden to give bipartisan negotiations more time comes as the president has shown signs of impatience as the more liberal wing of his party considers passing the relief package through a process known as budget reconciliation. That would allow the bill to advance with only the backing of his Democratic majority. The Republicans did not provide many details of their proposal. One of the signatories, Louisiana Sen. Bill Cassidy, said that it would cost about $600 billion. “If you can’t find bipartisan compromise on COVID-19, I don’t know where you can find it,” said Ohio Sen. Rob Portman, who also signed the letter. The other GOP senators are Susan Collins of Maine, Lisa Murkowski of Alaska, Mitt Romney of Utah, Shelley Moore Capito of West Virginia, Todd Young of Indiana, Jerry Moran of Kansas, Mike Rounds of South Dakota, and Thom Tillis of North Carolina. Brian Deese, the top White House economic adviser who is leading the administration’s outreach to Congress, said administration officials were reviewing the letter. He did not immediately commit to a Biden meeting with the lawmakers. But Cedric Richmond, a senior Biden adviser, said the president “is very willing to meet with anyone to advance the agenda.” When asked about the senators’ plan, Richmond said, “this is about seriousness of purpose.” Deese indicated the White House could be open to negotiating on further limiting who would receive stimulus checks. Portman suggested the checks should go to individuals who make no more than $50,000 per year and families capped at $100,000 per year. Under the Biden plan, families with incomes up to $300,000 could receive some stimulus money. “That is certainly a place that we’re willing to sit down and think about, are there ways to make the entire package more effective?” Deese said. As a candidate, Biden predicted his decades in the Senate and his eight years as Barack Obama’s vice president gave him credibility as a deal-maker and would help him bring Republicans and Democrats to consensus on the most important matters facing the country. But less than two weeks into his presidency, Biden showed frustration with the pace of negotiations at a time when the economy exhibited further evidence of wear from the pandemic. Last week, 847,000 Americans applied for unemployment benefits, a sign that layoffs remain high as the coronavirus pandemic continues to rage. “I support passing COVID relief with support from Republicans if we can get it. But the COVID relief has to pass — no ifs, ands or buts,” Biden said on Friday. In the letter, the Republican lawmakers reminded Biden that in his inaugural address, he proclaimed that the challenges facing the nation require “the most elusive of things in a democracy: Unity.” Cassidy separately criticized the current Biden plan as “chock-full of handouts and payoffs to Democratic constituency groups.” “You want the patina of bipartisanship … so that’s not unity,” Cassidy said. Jared Bernstein, a member of the White House Council of Economic Advisers, said Biden remains willing to negotiate but that officials needed to see more details from Republicans. At the same time, Bernstein pressed the administration’s argument that doing too little to stimulate the economy could have enormous impact on the economy in the near- and long-term. “Look, the American people really couldn’t care less about budget process, whether it’s regular order, bipartisanship, whether it’s filibuster, whether it’s reconciliation,” Bernstein said. “They need relief, and they need it now.” Portman and Deese were on CNN’s “State of the Union,” and Deese also was interviewed on NBC’s “Meet the Press.” Cassidy and Bernstein appeared on ”Fox News Sunday” and Richmond was on CBS’ “Face the Nation.” Republished with the permission of the Associated Press.
GOP largely sides against holding Donald Trump impeachment trial
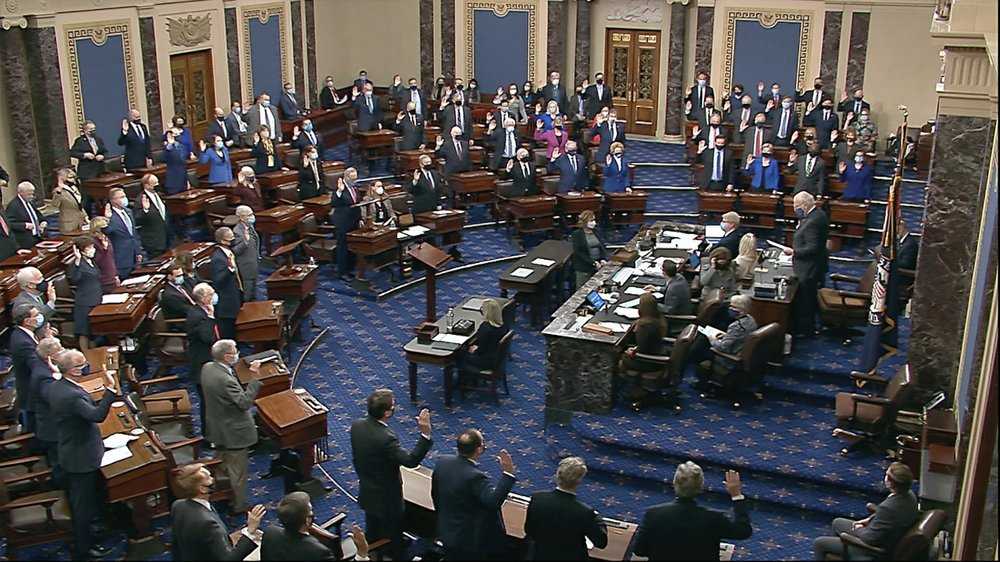
All but five Senate Republicans voted in favor of an effort to dismiss Donald Trump’s historic second impeachment trial on Tuesday, making clear a conviction of the former president for “incitement of insurrection” after the deadly Capitol siege on Jan. 6 is unlikely. While the Republicans did not succeed in ending the trial before it began, the test vote made clear that Trump still has enormous sway over his party as he becomes the first former president to be tried for impeachment. Many Republicans have criticized Trump’s role in the attack — before which he told his supporters to “fight like hell” to overturn his defeat — but most of them have rushed to defend him in the trial. “I think this was indicative of where a lot of people’s heads are,” said South Dakota Sen. John Thune, the No. 2 Republican in the Senate, after the vote. Late Tuesday, the presiding officer at the trial, Sen. Patrick Leahy, D-Vt., was taken to the hospital for observation after not feeling well at his office, spokesman David Carle said in a statement. The 80-year-old senator was examined by the Capitol’s attending physician, who recommended he be taken to the hospital out of an abundance of caution, he said. Later Tuesday, Carle said Leahy had been sent home “after a thorough examination” and was looking forward to getting back to work. Leahy presided over the trial’s first procedural vote, a 55-45 tally that saw the Senate set aside an objection from Kentucky Sen. Rand Paul that would have declared the impeachment proceedings unconstitutional and dismissed the trial. The vote means the trial on Trump’s impeachment will begin as scheduled the week of Feb. 8. The House impeached him Jan. 13, just a week after the deadly insurrection in which five people died. What seemed for some Democrats like an open-and-shut case that played out for the world on live television is running into a Republican Party that feels very different. Not only do senators say they have legal concerns, but they are wary of crossing the former president and his legions of followers. It’s unclear if any Republicans would vote to convict Trump on the actual charge of incitement after voting in favor of Paul’s effort to declare it unconstitutional. Ohio Sen. Rob Portman said after the vote that he had not yet made up his mind, and that constitutionality “is a totally different issue” than the charge itself. But many others indicated that they believe the final vote will be similar. The vote shows that “they’ve got a long ways to go to prove it,” Iowa Sen. Joni Ernst said of House Democrats’ charge. South Carolina Sen. Lindsey Graham, a close Trump ally, said he thinks the vote was “a floor not a ceiling.” Oklahoma Sen. James Lankford said he thinks that most Republicans will not see daylight between the constitutionality and the article of incitement. “You’re asking me to vote in a trial that by itself on its own is not constitutionally allowed?” he asked. Conviction would require the support of all Democrats and 17 Republicans, or two-thirds of the Senate — far from the five Republicans who voted with Democrats Tuesday to allow the trial to proceed. They were Sens. Susan Collins of Maine, Lisa Murkowski of Alaska, Mitt Romney of Utah, Ben Sasse of Nebraska and Pat Toomey of Pennsylvania — all recent critics of the former president and his effort to overturn President Joe Biden’s win. Senate Republican Leader Mitch McConnell, who has said Trump “provoked” the riots and indicated he is open to conviction, voted with Paul to move toward dismissing the trial. Democrats rejected the argument that the trial is illegitimate or unconstitutional because Trump is no longer in office, pointing to an 1876 impeachment of a secretary of war who had already resigned and to the opinions of many legal scholars. Democrats also say that a reckoning of the first invasion of the Capitol since the War of 1812, perpetrated by rioters egged on by a president as Electoral College votes were being tallied, is necessary. “It makes no sense whatsoever that a president, or any official, could commit a heinous crime against our country and then defeat Congress’ impeachment powers — and avoid a vote on disqualification — by simply resigning, or by waiting to commit that offense until their last few weeks in office,” said Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer. Before the vote, the senators officially opened the trial by taking oaths to ensure “impartial justice” as jurors. The nine House Democrats prosecuting the case against Trump carried the sole impeachment charge across the Capitol on Monday evening in a solemn and ceremonial march along the same halls the rioters ransacked three weeks ago. The lead House prosecutor, Rep. Jamie Raskin of Maryland, stood before the Senate to describe the violent events of Jan. 6 and read the House resolution charging “high crimes and misdemeanors.” For Democrats the tone, tenor, and length of the trial so early in Biden’s presidency poses its own challenge, forcing them to strike a balance between their vow to hold Trump accountable and their eagerness to deliver on the new administration’s priorities following their sweep of control of the House, Senate, and White House. Chief Justice John Roberts is not presiding at the trial, as he did during Trump’s first impeachment, potentially affecting the gravitas of the proceedings. The shift is said to be in keeping with protocol because Trump is no longer in office. Instead, Leahy, who serves in the largely ceremonial role of Senate president pro tempore, was sworn in on Tuesday. Leaders in both parties agreed to a short delay in the proceedings, which serves their political and practical interests, even as National Guard troops remain at the Capitol because of security threats to lawmakers ahead of the trial. The start date gives Trump’s still-evolving legal team time to prepare its case, while also providing more than a month’s distance from the passions
Donald Trump impeached after Capitol riot in historic second charge

President Donald Trump was impeached by the U.S. House for a historic second time Wednesday, charged with “incitement of insurrection” over the deadly mob siege of the Capitol in a swift and stunning collapse of his final days in office. With the Capitol secured by armed National Guard troops inside and out, the House voted 232-197 to impeach Trump. The proceedings moved at lightning speed, with lawmakers voting just one week after violent pro-Trump loyalists stormed the U.S. Capitol after the president’s calls for them to “fight like hell” against the election results. Ten Republicans fled Trump, joining Democrats who said he needed to be held accountable and warned ominously of a “clear and present danger” if Congress should leave him unchecked before Democrat Joe Biden’s inauguration Jan. 20. Trump is the only U.S. president to be twice impeached. It was the most bipartisan presidential impeachment in modern times, more so than against Bill Clinton in 1998. The Capitol insurrection stunned and angered lawmakers, who were sent scrambling for safety as the mob descended, and it revealed the fragility of the nation’s history of peaceful transfers of power. The riot also forced a reckoning among some Republicans, who have stood by Trump throughout his presidency and largely allowed him to spread false attacks against the integrity of the 2020 election. House Speaker Nancy Pelosi invoked Abraham Lincoln and the Bible, imploring lawmakers to uphold their oath to defend the Constitution from all enemies, foreign “and domestic.” She said of Trump: “He must go, he is a clear and present danger to the nation that we all love.” Holed up at the White House, watching the proceedings on TV, Trump took no responsibility for the bloody riot seen around the world, but issued a statement urging “NO violence, NO lawbreaking and NO vandalism of any kind” to disrupt Biden’s ascension to the White House. In the face of the accusations against him and with the FBI warning of more violence, Trump said, “That is not what I stand for, and it is not what America stands for. I call on ALL Americans to help ease tensions and calm tempers.” Trump was first impeached by the House in 2019 over his dealings with Ukraine, but the Senate voted in 2020 acquit. He is the first to be impeached twice. None has been convicted by the Senate, but Republicans said Wednesday that could change in the rapidly shifting political environment as officeholders, donors, big business and others peel away from the defeated president. The soonest Republican Senate leader Mitch McConnell would start an impeachment trial is next Tuesday, the day before Trump is already set to leave the White House, McConnell’s office said. The legislation is also intended to prevent Trump from ever running again. McConnell believes Trump committed impeachable offenses and considers the Democrats’ impeachment drive an opportunity to reduce the divisive, chaotic president’s hold on the GOP, a Republican strategist told The Associated Press on Wednesday. McConnell told major donors over the weekend that he was through with Trump, said the strategist, who demanded anonymity to describe McConnell’s conversations. In a note to colleagues Wednesday, McConnell said he had “not made a final decision on how I will vote.” Unlike his first time, Trump faces this impeachment as a weakened leader, having lost his own reelection as well as the Senate Republican majority. Even Trump ally Kevin McCarthy, the House Republican leader, shifted his position and said Wednesday the president bears responsibility for the horrifying day at the Capitol. In making a case for the “high crimes and misdemeanors” demanded in the Constitution, the four-page impeachment resolution approved Wednesday relies on Trump’s own incendiary rhetoric and the falsehoods he spread about Biden’s election victory, including at a rally near the White House on the day of the Jan. 6 attack on the Capitol. A Capitol Police officer died from injuries suffered in the riot, and police shot and killed a woman during the siege. Three other people died in what authorities said were medical emergencies. The riot delayed the tally of Electoral College votes which was the last step in finalizing Biden’s victory. Ten Republican lawmakers, including third-ranking House GOP leader Liz Cheney of Wyoming, voted to impeach Trump, cleaving the Republican leadership, and the party itself. Cheney, whose father is the former Republican vice president, said of Trump’s actions summoning the mob that “there has never been a greater betrayal by a President” of his office. Trump was said to be livid with perceived disloyalty from McConnell and Cheney. With the team around Trump hollowed out and his Twitter account silenced by the social media company, the president was deeply frustrated that he could not hit back, according to White House officials and Republicans close to the West Wing who weren’t authorized to speak publicly about private conversations. From the White House, Trump leaned on Sen. Lindsey Graham of South Carolina to push Republican senators to resist, while chief of staff Mark Meadows called some of his former colleagues on Capitol Hill. The president’s sturdy popularity with the GOP lawmakers’ constituents still had some sway, and most House Republicans voted not to impeach. Security was exceptionally tight at the Capitol, with tall fences around the complex. Metal-detector screenings were required for lawmakers entering the House chamber, where a week earlier lawmakers huddled inside as police, guns drawn, barricade the door from rioters. “We are debating this historic measure at a crime scene,” said Rep. Jim McGovern, D-Mass. During the debate, some Republicans repeated the falsehoods spread by Trump about the election and argued that the president has been treated unfairly by Democrats from the day he took office. Other Republicans argued the impeachment was a rushed sham and complained about a double standard applied to his supporters but not to the liberal left. Some simply appealed for the nation to move on. Rep. Tom McClintock of California said, “Every movement has a lunatic fringe.” Yet Democratic Rep. Jason Crow, D-Colo. and others recounted the harrowing
Donald Trump faces ‘incitement of insurrection’ impeachment charge

As the House prepares for impeachment, President Donald Trump faces a single charge — “incitement of insurrection” — over the deadly riot at the U.S. Capitol, according to a draft of the articles obtained by The Associated Press. Lawmakers are set to introduce the legislation Monday, with voting mid-week. Pelosi’s leadership team also will seek a quick vote on a resolution calling on Vice President Mike Pence and Cabinet officials to invoke the 25th Amendment. The four-page impeachment bill draws from Trump’s own false statements about his election defeat to Democrat Joe Biden; his pressure on state officials in Georgia to “find” him more votes; and his White House rally ahead of the Capitol siege, in which he encouraged thousands of supporters to “fight like hell” before they stormed the building on Wednesday. A violent and largely white mob of Trump supporters overpowered police, broke through security lines and windows, and rampaged through the Capitol, forcing lawmakers to scatter as they were finalizing Biden’s victory over Trump in the Electoral College. “President Trump gravely endangered the security of the United States and its institutions of Government,” the legislation said. The bill from Reps. David Cicilline of Rhode Island, Ted Lieu of California, Jamie Raskin of Maryland, and Jerrold Nadler of New York, said Trump threatened “the integrity of the democratic system, interfered with the peaceful transition of power” and “betrayed” trust. “He will remain a threat to national security, democracy, and the Constitution if allowed to remain in office,” they wrote. Rep. Adam Schiff, D-Ca., said Monday on CBS, “We need to move forward with alacrity.” House Speaker Nancy Pelosi says the House will proceed with legislation to impeach Trump as she pushes the vice president and the Cabinet to invoke constitutional authority to force him out, warning that Trump is a threat to democracy after the deadly assault on the Capitol. A Republican senator, Pat Toomey of Pennsylvania, joined Republican Sen. Lisa Murkowski of Alaska over the weekend in calling for Trump to “resign and go away as soon as possible.” Lawmakers warned of the damage the president could still do before Joe Biden is inaugurated Jan. 20. Trump, holed up at the White House, was increasingly isolated after a mob rioted in the Capitol in support of his false claims of election fraud. Judges across the country, including some nominated by Trump, repeatedly dismissed cases and Attorney General William Barr, a Trump ally, said there was no sign of any widespread fraud. “We will act with urgency, because this President represents an imminent threat,” Pelosi said in a letter late Sunday to colleagues emphasizing the need for quick action. “The horror of the ongoing assault on our democracy perpetrated by this President is intensified and so is the immediate need for action.” During an interview on “60 Minutes” aired Sunday, Pelosi invoked the Watergate era when Republicans in the Senate told President Richard Nixon, “It’s over.” “That’s what has to happen now,” she said. Pence has given no indication he would act on the 25th Amendment. If he does not, the House would move toward impeachment. Toomey said he doubted impeachment could be done before Biden is inaugurated, even though a growing number of lawmakers say that step is necessary to ensure Trump can never hold elected office again. “I think the president has disqualified himself from ever, certainly, serving in office again,” Toomey said. “I don’t think he is electable in any way.” Murkowski, long exasperated with the president, told the Anchorage Daily News on Friday that Trump simply “needs to get out.” A third, Sen. Roy Blunt, R-Mo., did not go that far, but on Sunday he warned Trump to be “very careful” in his final days in office. On impeachment, House Democrats would likely delay for 100 days sending articles of impeachment to the Senate for trial, to allow Biden to focus on other priorities. Sen. Marco Rubio, R-Fla., said that instead of coming together, Democrats want to “talk about ridiculous things like ‘Let’s impeach a president’” with just days left in office. Still, some Republicans might be supportive. Nebraska Sen. Ben Sasse said he would take a look at any articles that the House sent over. Illinois Rep. Adam Kinzinger, a frequent Trump critic, said he would “vote the right way” if the matter were put in front of him. The Democratic effort to stamp Trump’s presidential record — for the second time — with the indelible mark of impeachment advanced rapidly after the riot. Rep. David Cicilline, D-R.I, a leader of the House effort to draft impeachment articles accusing Trump of inciting insurrection, said Sunday that his group had 200-plus co-sponsors. Potentially complicating Pelosi’s decision about impeachment was what it meant for Biden and the beginning of his presidency. While reiterating that he had long viewed Trump as unfit for office, Biden on Friday sidestepped a question about impeachment, saying what Congress did “is for them to decide.” Republished with the permission of the Associated Press.
Dividing party, Republicans poised to challenge Joe Biden win

Republicans mounting an unprecedented challenge to Joe Biden’s election win are setting up a congressional showdown on Wednesday that threatens to divide their party and the country for years to come. With protestors already gathering in Washington to support President Donald Trump, the House and the Senate will convene a joint session to count the electoral votes cast in November’s election. Trump has repeatedly said there was widespread fraud, but his claims have been roundly rejected by Republican and Democratic election officials in state after state and by judges, including at the Supreme Court, further cementing Biden’s victory. Trump sees the joint session of Congress as one of his final attempts to overturn the results, even though there is no credible path for that to happen. Echoing Trump’s baseless claims, some of his Republican allies in Congress plan to formally object to the results, focusing on six battleground states — Arizona, Georgia, Michigan, Nevada, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin. But a growing number of their GOP colleagues, especially in the Senate, said they would not sign on. If an objection has support from both a House member and a senator in writing, then both chambers will vote on it. That could happen three or more times on Wednesday as Republican Sens. Josh Hawley of Missouri, Ted Cruz of Texas, and Kelly Loeffler of Georgia, along with at least ten other GOP senators, have indicated they will support at least some of the House challenges. It is unclear just what the Republican senators will do, but the process could drag into the night as the two chambers will have to consider each objection individually. There could be more than 100 Republicans in the House willing to object. The challenge to the presidential election is on a scale unseen since the aftermath of the Civil War, though the typically routine process of confirming Electoral College votes has been hit with brief objections before. In 2017, several House Democrats challenged Trump’s win, but Biden, who presided at the time as the vice president, swiftly dismissed them to assert Trump’s victory. In 2005, a challenge by a Democratic House member and a Democratic senator to George W. Bush’s victory in Ohio was quickly dismissed by both chambers. The effort this week is expected to be much broader but is all but certain to fail. Biden is set to be inaugurated Jan. 20. Republicans had not yet settled on a full strategy the night before the joint session. A late-night meeting on Monday convened by Cruz reached few conclusions, according to two Republicans familiar with the situation and granted anonymity to discuss it. Cruz will object to electoral results from Arizona, another Republican said — likely to be the first objection considered, in a state Biden won. Hawley has said he will object to the Pennsylvania results, and Loeffler may object to Georgia, where she was vying to keep her seat in a runoff election on Tuesday. With mounting desperation, Trump declared at a campaign rally for Loeffler and David Perdue in Georgia Monday that he would “fight like hell” to hold on to the presidency and he appealed to Republican lawmakers to reverse his election loss. Perdue is seeking another six years in the Senate, but his term expired Sunday. The days ahead will be defining for his presidency. Trump is whipping up crowds and people are gathering in Washington, where security is on alert. Lawmakers are being told to arrive early at the Capitol and some are considering sleeping overnight in their offices to ensure they can safely access the building amid the protests. Vice President Mike Pence will be closely watched as he presides over the session. He is under growing pressure from Trump and others to tip the results in Trump’s favor. But Pence has a ceremonial role that does not give him the power to affect the outcome. “I promise you this: On Wednesday, we’ll have our day in Congress,” Pence said while himself campaigning in Georgia ahead of Tuesday’s runoff elections that will determine control of the Senate. But he did not detail what that meant. The high-stakes decisions on whether to ally with Trump are splitting the Republican Party. A range of Republican officials — including Gov. Larry Hogan of Maryland; Rep. Liz Cheney of Wyoming, the third-ranking House GOP leader; and former House Speaker Paul Ryan — have criticized the GOP efforts to overturn the election. And more than a dozen Republican senators have said they will not support the effort. “The 2020 election is over,” said a statement Sunday from a bipartisan group of 10 senators, including Republicans Susan Collins of Maine, Lisa Murkowski of Alaska, Bill Cassidy of Louisiana, and Mitt Romney of Utah. Several others have said they, too, will not back objections, including Republican Sens. John Thune of South Dakota, the No. 2 Republican in the Senate who said last month he thought any challenges would go down “like a shot dog.” In a statement Tuesday, South Carolina Sen. Tim Scott said that as he reads the Constitution, “there is no constitutionally viable means for the Congress to overturn an election wherein the states have certified and sent their electors.” Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell has tried to prevent his party from engaging in the battle, which could help define the GOP in the post-Trump era and create lingering resentments among Republican voters. Both Hawley and Cruz are potential 2024 presidential contenders, vying for Trump’s base of supporters. Some other potential candidates, including Arkansas Sen. Tom Cotton, have chosen not to challenge the results. Cruz’s coalition of 13 senators has said it will vote to reject the Electoral College tallies unless Congress launches a commission to immediately conduct an audit of the election results. Congress is unlikely to agree to that. Facing the criticism from many in his own party, Cruz has attempted to put a finer point on his challenge. The commission remains his focus, he has said, not to undo the election
Republicans condemn ‘scheme’ to undo election for Donald Trump

The unprecedented Republican effort to overturn the presidential election has been condemned by an outpouring of current and former GOP officials warning the effort to sow doubt in Joe Biden’s win and keep President Donald Trump in office is undermining Americans’ faith in democracy. Trump has enlisted support from a dozen Republican senators and up to 100 House Republicans to challenge the Electoral College vote when Congress convenes in a joint session to confirm President-elect Joe Biden’s 306-232 win. With Biden set to be inaugurated Jan. 20, Trump is intensifying efforts to prevent the traditional transfer of power, ripping the party apart. Despite Trump’s claims of voter fraud, state officials have insisted the elections ran smoothly and there was no evidence of fraud or other problems that would change the outcome. The states have certified their results as fair and valid. Of the more than 50 lawsuits the president and his allies have filed challenging election results, nearly all have been dismissed or dropped. He’s also lost twice at the U.S. Supreme Court. On a call disclosed Sunday, Trump can be heard pressuring Georgia officials to “find” him more votes. But some senior lawmakers, including prominent Republicans, are pushing back. “The 2020 election is over,” said a statement Sunday from a bipartisan group of 10 senators, including Republicans Susan Collins of Maine, Lisa Murkowski of Alaska, Bill Cassidy of Louisiana, and Mitt Romney of Utah. The senators wrote that further attempts to cast doubt on the election are “contrary to the clearly expressed will of the American people and only serve to undermine Americans’ confidence in the already determined election results.” Republican Gov. Larry Hogan of Maryland said, “The scheme by members of Congress to reject the certification of the presidential election makes a mockery of our system and who we are as Americans.” Former House Speaker Paul Ryan, a Republican, said in a statement that “Biden’s victory is entirely legitimate” and that efforts to sow doubt about the election “strike at the foundation of our republic.” Rep. Liz Cheney of Wyoming, the third-ranking House Republican, warned in a memo to colleagues that objections to the Electoral College results “set an exceptionally dangerous precedent.” One of the more outspoken conservatives in Congress, Arkansas Republican Sen. Tom Cotton, said he will not oppose the counting of certified electoral votes on Jan. 6. “I’m grateful for what the president accomplished over the past four years, which is why I campaigned vigorously for his reelection. But objecting to certified electoral votes won’t give him a second term—it will only embolden those Democrats who want to erode further our system of constitutional government.” Cotton said he favors further investigation of any election problems, separate from the counting of the certified Electoral College results. Other prominent former officials also criticized the ongoing attack on election results. In a brief op-ed in The Washington Post, the 10 living former defense secretaries — half who served Republican presidents — said “the time for questioning the results has passed; the time for the formal counting of the electoral college votes, as prescribed in the Constitution and statute, has arrived.” The unusual challenge to the presidential election, on a scale unseen since the aftermath of the Civil War, clouded the opening of the new Congress and is set to consume its first days. The House and Senate will meet Wednesday in a joint session to accept the Electoral College vote, a typically routine process that’s now expected to be a prolonged fight. Trump is refusing to concede, and pressure is mounting on Vice President Mike Pence to ensure victory while presiding in what is typically a ceremonial role over the congressional session. Trump is whipping up crowds for a rally in Washington. The president tweeted Sunday against the election tallies and Republicans not on his side. Biden’s transition spokesman, Mike Gwin, dismissed the senators’ effort as a “stunt” that won’t change the fact that Biden will be sworn in Jan. 20. House Speaker Nancy Pelosi said in a letter to colleagues that while there is “no doubt” of Biden’s victory, their job now “is to convince more of the American people to trust in our democratic system.” The effort in the Senate was being led by Sens. Josh Hawley, R-Mo., and Ted Cruz, R-Texas. Hawley defended his actions in a lengthy email to colleagues, explaining that his Missouri constituents have been “loud and clear” with their belief that Biden’s defeat of Trump was unfair. “It is my responsibility as a senator to raise their concerns,” Hawley wrote late Saturday. Hawley plans to object to the state tally from Pennsylvania. But that state’s Republican senator, Pat Toomey, criticized the attack on Pennsylvania’s election system and said the results that named Biden the winner are valid. Cruz’s coalition of 11 Republican senators vows to reject the Electoral College tallies unless Congress launches a commission to immediately conduct an audit of the election results. They are zeroing in on the states where Trump has raised unfounded claims of voter fraud. Congress is unlikely to agree to their demand. The group, which presented no new evidence of election problems, includes Sens. Ron Johnson of Wisconsin, James Lankford of Oklahoma, Steve Daines of Montana, John Kennedy of Louisiana, Marsha Blackburn of Tennessee, and Mike Braun of Indiana. New senators in the group are Cynthia Lummis of Wyoming, Roger Marshall of Kansas, Bill Hagerty of Tennessee, and Tommy Tuberville of Alabama. The convening of the joint session to count the Electoral College votes has faced objections before. In 2017, several House Democrats challenged Trump’s win but Biden, who presided at the time as the vice president, swiftly dismissed them to assert Trump’s victory. Rarely have the protests approached this level of intensity. The moment is a defining one for the Republican Party in a post-Trump era. Both Hawley and Cruz are potential 2024 presidential contenders, cementing their alignment with Trump’s base of supporters. Others are trying to forge a different path for the GOP. Pence will be carefully watched as he presides over what is expected
More GOP lawmakers enlist in Donald Trump’s effort to undo Joe Biden’s win
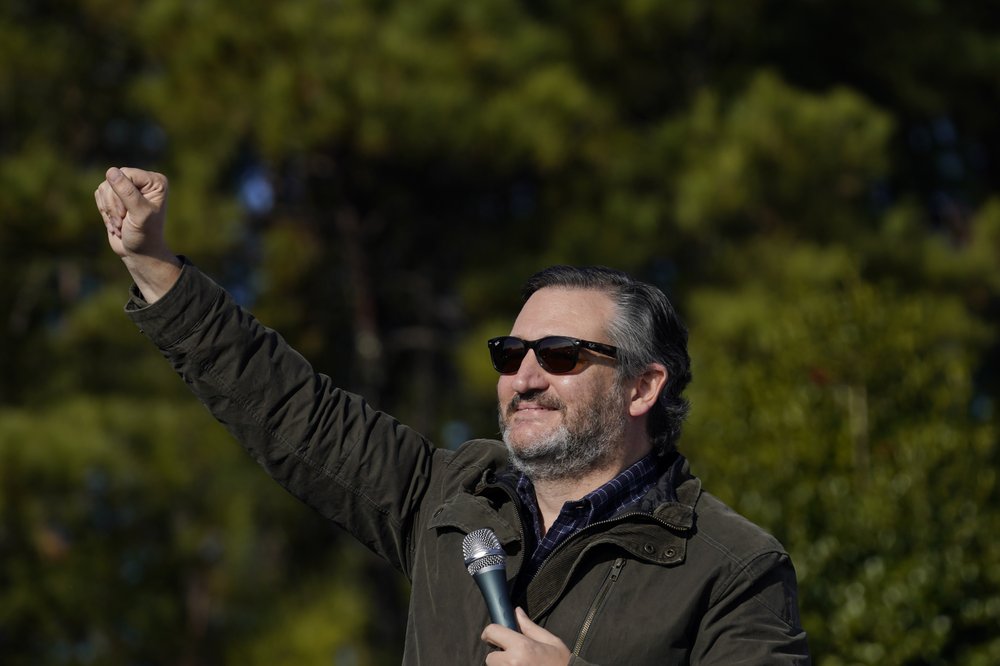

A growing number of Republican lawmakers are joining President Donald Trump’s extraordinary effort to overturn the election, pledging to reject the results when Congress meets next week to count the Electoral College votes and certify President-elect Joe Biden’s win. Sen. Ted Cruz of Texas on Saturday announced a coalition of 11 senators and senators-elect who have been enlisted for Trump’s effort to subvert the will of American voters. This follows the declaration from Sen. Josh Hawley of Missouri, who was the first to buck Senate leadership by saying he would join with House Republicans in objecting to the state tallies during Wednesday’s joint session of Congress. Trump’s refusal to accept his defeat is tearing the party apart as Republicans are forced to make consequential choices that will set the contours of the post-Trump era. Hawley and Cruz are both among potential 2024 presidential contenders. Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell had urged his party not to try to overturn what nonpartisan election officials have concluded was a free and fair vote. The 11 senators largely acknowledged Saturday they will not succeed in preventing Biden from being inaugurated on Jan. 20 after he won the Electoral College 306-232. But their challenges, and those from House Republicans, represent the most sweeping effort to undo a presidential election outcome since the Civil War. (Jan. 1) “We do not take this action lightly,” Cruz and the other senators said in a joint statement. They vowed to vote against certain state electors on Wednesday unless Congress appoints an electoral commission to immediately conduct an audit of the election results. They are zeroing in on the states where Trump has raised unfounded claims of voter fraud. Congress is unlikely to agree to their demand. The group, which presented no new evidence of election problems, includes Sens. Ron Johnson of Wisconsin, James Lankford of Oklahoma, Steve Daines of Montana, John Kennedy of Louisiana, Marsha Blackburn of Tennessee and Mike Braun of Indiana, and Sens.-elect Cynthia Lummis of Wyoming, Roger Marshall of Kansas, Bill Hagerty of Tennessee and Tommy Tuberville of Alabama. Trump, the first president to lose a reelection bid in almost 30 years, has attributed his defeat to widespread voter fraud, despite the consensus of nonpartisan election officials and even Trump’s attorney general that there was none. Of the roughly 50 lawsuits the president and his allies have filed challenging election results, nearly all have been dismissed or dropped. He’s also lost twice at the U.S. Supreme Court. The days ahead are expected to do little to change the outcome. “Joe Biden will be inaugurated on January 20th, and no publicity stunt will change that,” said Sen. Amy Klobuchar of Minnesota, the top Democrat on the panel overseeing the Electoral College count. Klobuchar said the Republican effort to create a federal commission “to supersede state certifications” is wrong. “It is undemocratic. It is un-American. And fortunately, it will be unsuccessful. In the end, democracy will prevail,” she said in a statement. The convening of the joint session to count the Electoral College votes is usually routine. While objections have surfaced before — in 2017, several House Democrats challenged Trump’s win — few have approached this level of intensity. On the other side of the Republican divide, several senators spoke out Saturday against Cruz and Hawley’s effort. Sen. Lisa Murkowski of Alaska said in a statement that she will vote to affirm the election and urged colleagues in both parties to join her in “maintaining confidence” in elections “so that we ensure we have the continued trust of the American people.” Sen. Pat Toomey of Pennsylvania said a “fundamental, defining feature of a democratic republic is the right of the people to elect their own leaders.” He said the effort by Hawley, Cruz, and others “to overturn the results of the 2020 presidential election in swing states like Pennsylvania directly undermines this right.” Earlier this week, Sen. Ben Sasse of Nebraska, another possible 2024 contender, urged his colleagues to “reject this dangerous ploy,” which he said threatens the nation’s civic norms. Caught in the middle is Vice President Mike Pence, who faces growing pressure from Trump’s allies over his ceremonial role in presiding over the session Wednesday. His chief of staff, Marc Short, said in a statement Saturday that Pence “welcomes the efforts of members of the House and Senate to use the authority they have under the law to raise objections.” Several Republicans have indicated they are under pressure from constituents back home to show they are fighting for Trump in his baseless campaign to stay in office. Sen. John Thune, the second-ranking Republican, told reporters at the Capitol that leadership was allowing senators to “vote their conscience.” Thune’s remarks as the GOP whip in charge of rounding up votes show that Republican leadership is not putting its muscle behind Trump’s demands, but allowing senators to choose their course. He noted the gravity of questioning the election outcome. “This is an issue that’s incredibly consequential, incredibly rare historically, and very precedent-setting,” he said. “This is a big vote.” Pence will be carefully watched as he presides over what is typically a routine vote count in Congress but is now heading toward a prolonged showdown that could extend into Wednesday night, depending on how many challenges are mounted. A judge in Texas dismissed a lawsuit from Rep. Louie Gohmert, R-Texas, and a group of Arizona electors trying to force Pence to step outside mere ceremony and shape the outcome of the vote. U.S. District Judge Jeremy Kernodle, a Trump appointee, dismissed the suit late Friday. To ward off a dramatic unraveling, McConnell convened a conference call with Republican senators Thursday specifically to address the coming joint session and logistics of tallying the vote, according to several Republicans granted anonymity to discuss the private call. The Republican leader pointedly called on Hawley to answer questions about his challenge to Biden’s victory, according to two of the Republicans. But there was no response because Hawley was a no-show, the Republicans
U.S. to get 9th justice with Dems powerless to block Amy Coney Barrett

A divided Senate is set to confirm Amy Coney Barrett to the Supreme Court, giving the country a ninth justice Monday as Republicans overpower Democratic opposition to secure President Donald Trump’s nominee the week before Election Day. Democratic leaders asked Vice President Mike Pence to stay away from presiding over her Senate confirmation due to potential health risks after his aides tested positive for COVID-19. But although Pence isn’t needed to break a tie, the vote would present a dramatic opportunity for him to preside over confirmation of Trump’s third Supreme Court justice. Senate Democratic leader Chuck Schumer and his leadership team wrote that not only would Pence’s presence violate Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines, “it would also be a violation of common decency and courtesy.” But Senate Republicans control the chamber and Barrett’s confirmation isn’t in doubt. The 48-year-old Barrett would secure a conservative court majority for the foreseeable future, potentially opening a new era of rulings on abortion, gay marriage, and the Affordable Care Act. A case against the Obama-era health law is scheduled to be heard Nov. 10. Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell scoffed at the “apocalyptic” warnings from critics that the judicial branch was becoming mired in partisan politics as he defended its transformation under his watch. “This is something to be really proud of and feel good about,” the Republican leader said Sunday during a rare weekend session. McConnell said that unlike legislative actions that can be undone by new presidents or lawmakers, “they won’t be able to do much about this for a long time to come.” Schumer, of New York, said the Trump administration’s drive to install Barrett during the coronavirus crisis shows “the Republican Party is willing to ignore the pandemic in order to rush this nominee forward.” To underscore the potential health risks, Schumer urged his colleagues Sunday not to linger in the chamber but “cast your votes quickly and from a safe distance.” Some GOP senators tested positive for the coronavirus following a Rose Garden event with Trump to announce Barrett’s nomination, but they have since said they have been cleared by their doctors from quarantine. Pence’s office said the vice president tested negative for the virus on Monday. The confirmation was expected to be the first of a Supreme Court nominee so close to a presidential election. It’s also one of the first high court nominees in recent memory receiving no support from the minority party, a pivot from not long ago when a president’s picks often won wide support. Barrett presented herself in public testimony before the Senate Judiciary Committee as a neutral arbiter and suggested, “It’s not the law of Amy.” But her writings against abortion and a ruling on “Obamacare” show a deeply conservative thinker. She was expected to be seated quickly on the high court. “She’s a conservative woman who embraces her faith. She’s unabashedly pro-life, but she’s not going to apply ‘the law of Amy’ to all of us,” the Judiciary Committee chairman, Sen. Lindsey Graham, R-S.C., said on Fox News Channel. At the start of Trump’s presidency, McConnell engineered a Senate rules change to allow confirmation by a majority of the 100 senators, rather than the 60-vote threshold traditionally needed to advance high court nominees over objections. It was an escalation of a rules change Democrats put in place to advance other court and administrative nominees under President Barack Obama. On Sunday, the Senate voted 51-48 to begin to bring the process to a vote as senators, mostly Democrats, pulled an all-night session for the final 30 hours of often heated debate. Two Republicans, Lisa Murkowski of Alaska and Susan Collins of Maine, voted against advancing the nominee, and all Democrats who voted were opposed. California Sen. Kamala Harris, the vice presidential nominee, missed the vote while campaigning in Michigan. Monday’s final tally was expected to grow by one after Murkowski announced her support for the nominee, even as she decried filling the seat in the midst of a heated race for the White House. Murkowski said Saturday she would vote against the procedural steps but ultimately join GOP colleagues in confirming Barrett. “While I oppose the process that has led us to this point, I do not hold it against her,” Murkowski said. Collins, who faces a tight reelection fight in Maine, remains the only Republican expected to vote against Trump’s nominee. “My vote does not reflect any conclusion that I have reached about Judge Barrett’s qualifications to serve,” Collins said. “I do not think it is fair nor consistent to have a Senate confirmation vote prior to the election.” By pushing for Barrett’s ascension so close to the Nov. 3 election, Trump and his Republican allies are counting on a campaign boost, in much the way they believe McConnell’s refusal to allow the Senate to consider Barack Obama’s nominee in February 2016 created excitement for Trump among conservatives and evangelical Christians eager for a Republican president to replace the late Justice Antonin Scalia. Barrett was a professor at Notre Dame Law School when she was tapped by Trump in 2017 for an appeals court opening. Two Democrats joined at that time to confirm her, but none is expected to vote for her now. Republished with the permission of the Associated Press.


