Tommy Tuberville urges Senate investigation into human trafficking

U.S. Senator Tommy Tuberville (R-Alabama) joined Sen. Ron Johnson (R-Wisconsin), Sen. Katie Britt (R-Alabama), and the entire Senate Republican conference in sending a letter to Sens. Richard Blumenthal (D-Connecticut), who chairs the Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations; Richard Durbin (D-Illinois), who chairs the Committee on the Judiciary; Gary Peters (D-Michigan), who chairs the Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs; and Robert Menendez (D-New Jersey), who chairs the Committee on Foreign Relations, calling for increased oversight and investigations into human trafficking. The letter highlighted recent Department of Homeland Security (DHS) data underscoring the humanitarian crisis at the border. It also included a graph illustrating the rise in encounters at the southwest border. The senators wrote to the Democrat chairmen, “[g]iven your committees’ roles in overseeing DHS, we urge you to investigate and hold hearings into DHS’s efforts to combat human trafficking. Without our attention and leadership, human trafficking will continue to plague this country.” The senators noted that the recent movie Sound of Freedom (which is based on the true story of former Homeland Security Investigations agent Tim Ballard’s efforts to rescue victims from a Colombian sex-trafficking ring) “has played an important role in creating public awareness of this modern-day form of slavery.” “The United States Senate must continue to conduct much-needed oversight of this administration’s border policies to find immediate solutions to combat one of the most disturbing consequences of inadequate border security: the proliferation of human trafficking,” the Senators added. Tuberville was elected to the U.S. Senate in 2020 after a forty-year career as an educator, coach, and sports broadcaster. He is best known for his tenure as a college football head coach at Ole Miss, Auburn, Texas Tech, and Cincinnati. He represents Alabama in the United States Senate, where he is a member of the Senate Armed Services, Agriculture, Veterans Affairs, and HELP Committees. To connect with the author of this story or to comment, email brandonmreporter@gmail.com
$2T bill stalled, Senate Dems seem ready to move on for now

Democrats’ vast social and environment package was stuck in the Senate on Thursday as leaders’ hopes for an accord with holdout Sen. Joe Manchin and approval of their flagship domestic measure in the year’s waning days seemed all but dead. After a closed-door lunch among Senate Democrats, Sen. Ben Cardin, D-Md., told reporters that a statement by President Joe Biden was expected shortly giving an update on “his conversations with Sen. Manchin and others.” Talks on the 10-year, roughly $2 trillion bill between Biden and Manchin, who wants to cut and reshape the measure, are said to have yielded little progress. Majority Leader Chuck Schumer, D-N.Y., had set Senate passage before Christmas as his goal, but disputes with Manchin and other Democrats remain. It has become clear that the party is seeking explicit intervention from Biden in hopes he will cut a deal with Manchin, D-W.Va., or urge lawmakers to delay action until January. Biden “wants to get this done as soon as possible,” White House spokesperson Karine Jean-Pierre told reporters. She added, “But we understand it’s going to take time, and we’re going to continue to do the work.” Schumer barely mentioned the legislation as the day’s business began. Instead, he described Democrats’ efforts to break a logjam on voting rights legislation and a pile of nominations the Senate will consider “as we continue working to bring the Senate to a position where we can move forward” on the social and environment bill. Using his sway in a 50-50 Senate where Democrats need unanimity to prevail, Manchin has continued his drive to force his party to cut the bill’s cost and eliminate programs he opposes. All Republicans oppose the package, arguing the measure carrying many of Biden’s paramount domestic priorities is too expensive and would worsen inflation. “The best Christmas gift Washington could give working families would be putting this bad bill on ice,” said Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell, R-Ky. The rocky status of the Biden-Manchin talks was described Wednesday by a person who spoke only on condition of anonymity. The person said Manchin was pushing to eliminate the bill’s renewal of expanded benefits under the child tax credit, a keystone of Democratic efforts to reduce child poverty. Manchin told reporters Wednesday that assertions he wants to strip the child tax credit improvements were “a lot of bad rumors.” Asked if he backed eliminating one of the bill’s child tax credit improvements — monthly checks sent to millions of families — he said, “I’m not negotiating with any of you.” Adding further doubt about quick Senate action this year, Biden suggested that Democrats should instead prioritize voting rights legislation, a primary party goal that Republicans have long stymied. Democrats face an uphill fight on the voting measure, but focusing on it would let them wage a battle that energizes the party’s voters while lawmakers work behind the scenes on the social and environment bill. Asked whether Congress should quickly consider the voting legislation and delay the $2 trillion bill to next year, Biden told reporters, “If we can get the congressional voting rights done, we should do it.” He added, “There’s nothing domestically more important than voting rights.” Biden spoke Wednesday as he toured tornado damage in Dawson Springs, Kentucky. Letting the social and environment legislation slip into next year, when congressional elections will be held, would be ominous for the bill’s ultimate prospects. With Democrats having blown past previous self-imposed deadlines on the push, another delay would fuel Republican accusations that they are incompetently running a government they control. Democrats are bracing for November elections when the GOP has a real chance of winning control of the House and Senate. Word of Manchin’s stance prompted a backlash from colleagues, whom he’s frustrated for months with constant demands to cut the bill’s size and scope. The measure also has money for health care, universal prekindergarten, and climate change programs largely paid for with tax boosts on big corporations and the rich. The second-ranking Democrat, Sen. Richard Durbin of Illinois, said “the level of emotion” among Democrats over the child tax credit “is very high,” and said he was “stunned” when he heard about Manchin’s demands. Manchin has wanted the overall bill’s 10-year price tag to fall below $2 trillion. He also wants all its programs to last the full decade. The current bill would extend the enhanced child tax credit for just one year, a device to contain the bill’s cost. Renewing the improved benefits for ten years would increase its current one-year cost of around $100 billion to over $1 trillion, and doing that while cutting the overall bill’s size would wreak havoc on Democrats’ other priorities in the bill. The Treasury Department says the expanded tax credit has helped the families of 61 million children. Another impediment to Democrats is a time-consuming review by the Senate parliamentarian, Elizabeth MacDonough, about whether many of the bill’s provisions violate the chamber’s rules and should be dropped. Her written opinions on that, including on provisions letting many migrants remain temporarily in the U.S., may not be ready until the weekend or later. Manchin’s other demands have included removing a new requirement for paid family leave. Disputes among other lawmakers include how to increase federal tax deductions for state and local taxes. The House approved its version of the legislation in November. Republished with the permission of the Associated Press.
Minimum wage hike all but dead in big COVID relief bill
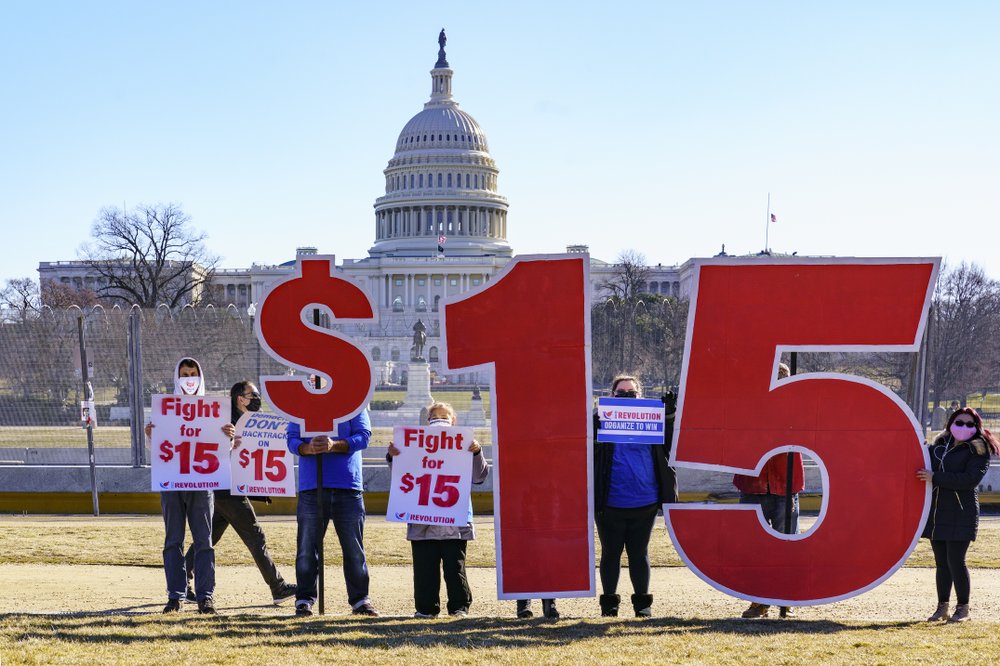
Democrats’ hopes of including a minimum wage increase in their $1.9 trillion COVID-19 relief bill seemed all but dead Monday as the Senate prepared to debate its own version of the House-passed aid package. Four days after the chamber’s parliamentarian said Senate rules forbid inclusion of a straight-out minimum wage increase in the relief measure, Democrats seemed to have exhausted their most realistic options for quickly salvaging the pay hike. In one decision, they abandoned a potential amendment threatening tax increases on big companies that don’t boost workers’ pay to certain levels. “At this moment, we may not have a path but I hope we can find one” for pushing the federal pay floor to $15 an hour, said No. 2 Senate Democratic leader Richard Durbin of Illinois. Senate Democrats hope to unveil their version of the broad relief package and begin debate as early as Wednesday. Congressional leaders want to send President Joe Biden the legislation combating the pandemic and bolstering the economy by March 14, the date emergency jobless benefits that lawmakers approved in December expire. The overall relief bill is Biden’s biggest early legislative priority. It looms as an initial test of his ability to unite Democrats in the Senate — where the party has no votes to spare — and risks lasting damage to his influence should he fail. Republicans are strongly against the legislation and could well oppose it unanimously, as House GOP lawmakers did when that chamber approved the bill early Saturday. The measure would provide $1,400 payments to individuals plus hundreds of billions of dollars for schools and colleges, COVID-19 vaccines and testing, mass transit systems, renters, and small businesses. It also has money for child care, tax breaks for families with children, and assistance for states willing to expand Medicaid coverage for low-income residents. Senate Budget Committee Chairman Bernie Sanders, I-Vt., said he wanted Democrats to ignore the parliamentarian’s ruling blocking the minimum wage increase. He also wants them to vote to eliminate filibusters — procedural delays that would take an unachievable 60 votes for Democrats to prevail. Neither idea seemed to have the support among Democrats or the White House needed to succeed. But Sanders, the Senate’s lead sponsor of the hike to $15, said he’d force a vote on an amendment restoring the minimum wage increase anyway. “This is the soul of the Democratic Party,” he said of the proposal. In an acknowledgment that his effort might fall short, he said, “If we fail in this legislation, I will be back” and offer it in the near future. The Senate is divided 50-50 between the parties with Vice President Kamala Harris able to cast only tie-breaking votes. Democrats are employing a seldom-used procedure for the COVID-19 relief bill that will shield the measure from filibusters. Biden discussed the relief bill Monday in a virtual meeting with nine Senate Democrats, including Joe Manchin of West Virginia, an opponent of the $15 hourly target. A White House statement said the group was “united in the goal of quickly passing a significant package that reflects the scope of the challenges our country is facing.” Democrats, who will need unanimity to pass the legislation, are pushing for several changes in the House measure. Manchin told reporters he wants the bill’s emergency unemployment benefits, set at $400 weekly by the House, to revert to the current $300 figure enacted in December. That is certain to be divisive and draw strong opposition from progressives. He and Sen. Jon Tester, D-Mont., also said they want spending to be better “targeted,” which Manchin said meant “helping the people that need help the most.” Republicans have said the legislation is too costly and spends money needlessly. Sen. Angus King, I-Maine, said he wants the bill’s $350 billion for state and local governments to specify minimum amounts for municipal governments and wants perhaps $50 billion to improve broadband coverage. The parliamentarian ruled Monday that some House-approved provisions, which would provide billions to help some struggling pension plans and to help people who’ve lost jobs afford health insurance, could stay in the bill, according to Senate Finance Committee Chairman Ron Wyden, D-Ore. The House-approved minimum wage language would gradually raise the federal floor to $15 an hour by 2025, more than double the $7.25 in place since 2009. After the parliamentarian said that provision would have to be deleted, Sanders and Wyden said they were working on plans to increase taxes on large corporations that don’t meet certain levels for workers’ pay. But that plan was dropped, Democrats said Monday, with Sanders saying the proposal would have been too easy for employers to evade. It was always questionable whether pressuring companies with tax increases would have won enough Democratic support to survive, and the idea would have affected only a fraction of workers paid the minimum wage. Raising the minimum wage has broad support among Democrats. But while it’s embraced passionately by the party’s progressives, at least two Senate moderates — Manchin and Kyrsten Sinema of Arizona — have voiced opposition to including it in the broader relief measure, wounding its prospects and fostering tensions within the party. Democrats must now decide “how we do minimum wage as part of another piece of legislation or on its own,” said Sen. Richard Blumenthal of Connecticut. While eliminating filibusters or overruling the parliamentarian has strong support among progressives, the ideas lack appeal to moderates. They are wary of erasing procedures that the party has used in the past, and could use again, to protect its priorities when it is in the minority. Among those who’ve long supported retaining the filibuster is Biden, who served nearly four decades in the Senate. “The president’s view on the filibuster is well known. He has not changed that point of view,” White House press secretary Jen Psaki said pointedly Monday. Republished with the permission of the Associate Press.
Richard Shelby says ‘The dialogue is good’ as wall deadline nears

President Donald Trump and House Speaker Nancy Pelosi struck starkly different tones in their border security standoff Wednesday, as Trump planned a rally in a Texas border city he says exemplifies the need for a wall and Pelosi said she’d back any bipartisan deal congressional bargainers produce. The contrasting pathways — with Trump set to appear before raucous supporters and Pelosi signaling compromise — came with just over a week until a Feb. 15 deadline for negotiators to reach agreement or potentially face a renewed partial government shutdown. House-Senate bargainers say their talks have become increasingly substantive and some lawmakers — including Pelosi herself — expressed hopes that negotiators might produce an accord as soon as Friday. Participants said the two sides were narrowing differences in their talks. Rep. Chuck Fleischmann, Republican-Tennessee, a negotiator, said Democrats were showing some flexibility in the semantic dispute over the type of physical barriers they would accept while Republicans seemed potentially willing to limit where the structures might be built. “That basically sets the stage for a very reasonable, flexible negotiation,” he said. Other unresolved questions include the amount to be spent on border security, and whether — as Democrats have proposed — to reduce the number of detention beds for migrants available to the federal Immigration and Customs Enforcement agency, Fleischmann said. “If they come up with a bipartisan agreement, I’m happy to support it,” Pelosi, Democrat-California, told reporters. She said she hoped Trump would take “the same hands off” approach. Democrats have been in a position of strength in the talks, after Republicans lost House control in November’s elections, Trump forced a record 35-day federal shutdown and surrendered without getting $5.7 billion he’s demanded for a wall. Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell, Republican- Kentucky, has also given bargainers a green light to seek a deal that he’s said he hopes Trump would find “worth signing.” If Pelosi and McConnell embrace a bipartisan agreement, it could isolate Trump and pressure him to accept it without re-escalating the fight. Trump has threatened a new shutdown or a declaration of a national emergency to access other budget funds if he’s not satisfied with a deal — steps members of both parties oppose. Bargainers met Wednesday privately for nearly two hours with federal border patrol and customs officials to hear their recommendations on how to secure the Southwest border. But several lawmakers emerged with differing conclusions. No. 2 Senate Democratic leader Richard Durbin said lawmakers were told the top priority was technology that could screen vehicles for drugs or migrants at border ports of entry. “They don’t rule out barriers, they don’t rule out fencing, but that isn’t the first priority,” Durbin told reporters. But Sen. Richard Shelby, Republican- Alabama, said the officials suggested a three-pronged approach using barriers, technology and personnel. He said the closed-door session was constructive. “The dialogue is good. The tone is good. We’re talking about substance,” Shelby said. He also said that in a phone conversation with Pelosi, “I just said, ‘Look, can we reach a yes on this in any way or are we wasting our time.’ She said, ‘No, keep working together,’ and she would like to see a legislative solution, the sooner the better.” In comments that suggested a potential avenue for agreement, some lawmakers suggested that giving local officials a say would be pivotal. “We can probably get there on some sort of enhanced barriers with local input,” said another negotiator, Rep. Henry Cuellar, Democrat-Texas. Democrats have proposed spending as much as $1.6 billion for border security including some types of physical barriers, but it remains unclear how much more money they’d accept as part of a deal. Cuellar said $5.7 billion for the wall is “not going to happen.” Meanwhile, the White House said Trump will hold his first campaign rally of the year next Monday in El Paso, Texas. His campaign manager, Brad Parscale, tweeted that the rally will be held “less than 1000 feet from the successful border fence that keeps El Paso safe!” In his State of the Union address Tuesday, Trump cited El Paso as once having “extremely high rates of violent crime. He asserted that with its wall, “El Paso is one of the safest cities in our country.” In fact, El Paso has never been considered one of the nation’s most dangerous cities and its trends in violent crime mirror national swings. In 2005, the city had a murder rate of 2.5 for every 100,000 residents, compared with a national rate of 5.6. By 2010 after the wall was built, El Paso’s murder rate had dropped to 0.9 for every 100,000 residents, compared with a national average of 4.8. Rep. Veronica Escobar, Democrat-Texas, tweeted that “El Paso has been one of the safest cities in the nation long before the wall was built in 2008. #WallsDontWork.” “El Paso is safe due to its people, the good community relations with law enforcement, and the trust of all communities in our local institutions,” Fernando Garcia, executive director of the Border Network for Human Rights, said in a statement. “El Pasoans should be offended by the way the president used our community to advance his racist and xenophobic agenda.” Republished with permission from the Associated Press
Week 1: Cabinet picks contradict Donald Trump stands on some issues

The lack of fireworks surrounding Senate consideration of President-elect Donald Trump‘s Cabinet picks may reflect a slew of statements his choices have made contradicting the billionaire businessman’s position on key issues. Trump acknowledged the differences early Friday, posting a message on his Twitter account saying: “All my Cabinet nominee are looking good and doing a great job. I want them to be themselves and express their own thoughts, not mine!” This week’s confirmation hearings produced an odd political chemistry where, for instance, one of the harshest examinations of a Trump Cabinet choice came from one of Trump’s fellow Republicans, presidential campaign rival Sen. Marco Rubio. Despite Democrats’ dismay over some of Trump’s selections, the hearings were relatively tranquil, with Democrats generally restrained even in quizzing the more contentious picks. The reason, according to a few Democrats: The nominees are proving more palatable than Trump himself. “As I meet members of the Cabinet I’m puzzled because many of them sound reasonable,” said Sen. Dick Durbin of Illinois, the No. 2 Senate Democrat. “Far more reasonable than their president.” That could change in weeks to come, because some of the most potentially explosive hearings are still pending, including the scrutiny of former Goldman Sachs partner Steven Mnuchin for Treasury secretary. Several of Trump’s Cabinet selections this week made statements this week contradicting policy stances espoused by their soon-to-be boss on issues ranging from Russia and NATO to climate change and Muslims. Sen. Jeff Sessions, picked for attorney general, said he’s against any outright ban on immigration by Muslims, in contrast to Trump’s onetime call to suspend admittance of Muslims until U.S. officials could learn more about nature of the threat of extremism. His secretary of state candidate, Rex Tillerson, took a relatively hard line on Washington’s dealings with Russia, even though Trump has been talking about improving relations between Washington and Moscow and held out for days before saying he accepted the intelligence community’s conclusion that Moscow meddled in the U.S. election process. Tillerson demurred, however, when one senator tried to lure him into calling President Vladimir Putin, whom he knows, a “war criminal,” although he emphasized support for NATO commitments that Trump had questioned. The secretary-of-state designate also said the United States should not back away from its efforts against nuclear proliferation, notwithstanding Trump’s suggestion earlier this year that some key U.S. allies like Japan and South Korea provide their own defense. Some of the toughest questioning of Tillerson came not from Democrats but from Rubio, who grilled the Exxon Mobil executive on human rights issues. As Mnuchin’s confirmation hearing approaches, Democrats have set up a website to solicit stories from the thousands of people whose homes were foreclosed on by OneWest Bank while he headed a group of investors who owned the bank. They hope to use Mnuchin’s nomination hearing to attack Trump’s populist appeal with working-class voters and cast themselves as defenders of the middle class. Thus far, though, Republicans are congratulating themselves for generally smooth sailing. And overall, the lack of drama may also be due to the decision by Democrats while in the Senate majority to lower the vote threshold for Cabinet nominees and others from 60 votes to 50, allowing Republicans to ensure approval as long as they can hold their 52-seat majority together. “The purpose of confirmation hearings is to examine the record and views of potential nominees and I think that’s what these hearings are doing,” said Sen. Ted Cruz, R-Texas. “I think it’s likely that all of the Cabinet nominees are going to be confirmed, I think the hearings have gone quite well this week.” A hearing Thursday for neurosurgeon Ben Carson to head the Department of Housing and Urban Development featured some pointed questioning from Massachusetts Sen. Elizabeth Warren, but also warm exchanges between Carson and other committee Democrats. Afterward Carson thanked the panel and said that it “was actually kind of fun.” Sessions was denied confirmation once before by the Senate, but that was three decades ago for a federal judgeship. This time around the Alabaman is a sitting senator and was treated gently, for the most part, by his colleagues, even when Democrats brought up the racial issues that brought him down him last time around. There was potential for drama as Sen. Cory Booker, D-N.J., broke with Senate tradition to testify against his colleague, but it came on the second day of the hearing after Sessions had finished testifying, so he was not even in the room. Tillerson had the rockiest outing thus far, with Rubio pressing him on Russia and Democratic Sen. Jeff Merkley of Oregon confronting him about climate change and other issues. With Rubio and others undecided on supporting Tillerson, his ultimate confirmation is in question. But even with Tillerson, Democrats seemed to pull their punches at times. “I don’t want to argue with you,” Sen. Tom Udall of New Mexico remarked at one point, seeming to speak for several colleagues. And it was practically bipartisan lovefests at the hearings for the choices for Central Intelligence Agency, Kansas Rep. Mike Pompeo; retired Gen. James Mattis for Defense; and retired Gen. John Kelly for Homeland Security. “Pompeo’s very popular, Mattis, Kelly — these are popular selections,” said Sen. John McCain, R-Ariz. The hearings seemed to underscore some emerging dynamics of Trump’s relations with Capitol Hill. Despite his highly unconventional approach, and his lack of Capitol Hill experience, many of his appointees and aides could have been selected by any other Republican, and the Senate is responding accordingly. And even where Trump’s surprising approach raises the potential for problems, congressional Republicans are working overtime to paper them over, not highlight them. “We are in complete sync,” House Speaker Paul Ryan, R-Wis., insisted Thursday in a discussion about a different topic, health care. That could change in weeks to come, as the Senate holds hearings on Mnuchin and other more divisive selections. These include conservative Rep. Tom Price for Health and Human Services; Oklahoma Attorney General Scott Pruitt,

